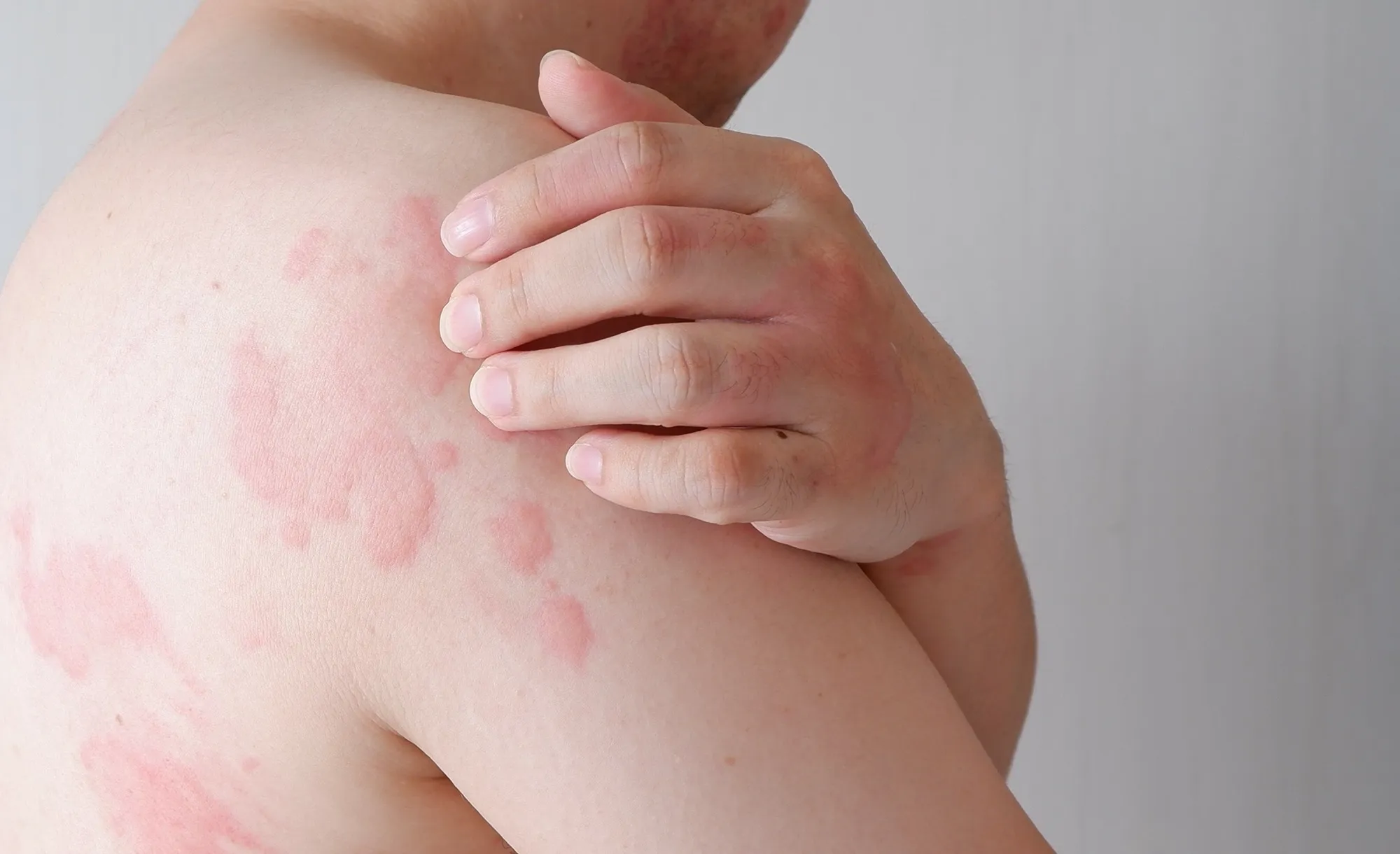
Urticaria, also known as hives, is a skin condition characterized by the formation of red or skin-colored welts, often accompanied by itching, swelling, and sometimes a burning or stinging sensation. These symptoms can develop rapidly and may last a few hours to several days. Moreover, the condition’s root causes vary and are often linked to the immune system’s response to specific triggers. Common causes include allergic reactions to foods, medications, or environmental factors, as well as infections, stress, and physical stimuli like temperature changes. In some cases, autoimmune disorders may lead to chronic Urticaria, where the immune system mistakenly targets healthy cells. Furthermore, the treatment for the condition typically involves identifying and avoiding the triggers, along with the use of antihistamines to reduce symptoms. Corticosteroids or other medications are often recommended in more serious cases to reduce inflammation and prevent recurrent outbreaks.
Urticaria can affect individuals of all ages, but it is more commonly seen in people with allergies or autoimmune conditions. If you experience early signs of the condition, it is important to seek professional help to identify the underlying problem and receive proper treatment. Furthermore, when being treated for Urticaria, you can expect your doctor to conduct a thorough evaluation, including a detailed history and possibly allergy testing. The treatment period varies based on the severity of the condition, but most cases are managed with medication and lifestyle adjustments within a few weeks. If you are experiencing symptoms of Urticaria, schedule an appointment at Omega Health Clinics in Modesto, CA, to receive personalized care and effective treatment options.
Urticaria, commonly known as hives, can be triggered by various factors. Common causes include allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect stings, or environmental allergens like pollen and pet dander. Non-allergic triggers, such as stress, exercise, infections, or exposure to high temperatures, can also cause hives. In some cases, the particular cause of Urticaria cannot be determined, which is referred to as Idiopathic Urticaria.
Diagnosing Urticaria involves a combination of clinical evaluation and patient history. Your healthcare provider will assess the appearance of the hives and ask about potential triggers, such as recent foods, medications, or stress levels. In some cases, a skin test for allergies may be necessary to identify specific allergens that could be causing the condition. Additionally, blood tests or other diagnostic procedures might be recommended if an underlying health condition is suspected.
Urticaria can become chronic in some cases. Chronic Urticaria is hives that last for six weeks or longer, often occurring daily or intermittently over months or years. Chronic Urticaria can be more challenging to treat, as the triggers may be harder to identify. Long-term management typically involves regular use of antihistamines and other medications to control symptoms and prevent flare-ups.
Urticaria is not contagious. Since Urticaria is related to a person’s specific immune response and not caused by a virus, bacteria, or other infectious agents, it cannot be passed on through contact, shared environments, or proximity to others. Each case of Urticaria is unique to the person experiencing it, and the welts or hives that appear are a direct result of the body’s reaction to particular stimuli, not something that can be caught or spread.
Certain lifestyle changes can help manage Urticaria and reduce the frequency of flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding known triggers is crucial. For example, if certain foods, stress, or temperature changes are known to cause hives, avoiding these can prevent outbreaks. Wearing loose, comfortable clothing, avoiding harsh soaps and skin irritants, and maintaining a cool, calm environment can also help. Moreover, an active lifestyle, a balanced diet, and stress management practices like yoga or meditation can contribute to overall health and potentially minimize the severity of symptoms.
If your symptoms worsen, it is crucial to seek medical attention promptly. Severe cases of Urticaria can lead to complications, such as angioedema, where deeper layers of the skin swell, often affecting the eyes, lips, or throat. In rare cases, this can develop into breathing concerns and require immediate medical care. If your hives become more widespread, if you experience difficulty swallowing or breathing, or if your symptoms do not improve with standard treatment, contact your doctor immediately for further evaluation and management.